Retrieving GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) Data
In this project you will be directed to retrieve GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) location and time data using an NB-LYNX-7000 board installed with a GPS Antenna.
Prerequisites
The materials required follow the General Prerequisites on the previous page. If you have not prepared the requirements on that page, then you can visit the following page.
General Prerequisites NB-Lynx-7000Follow These Steps
1. Equipment Setup
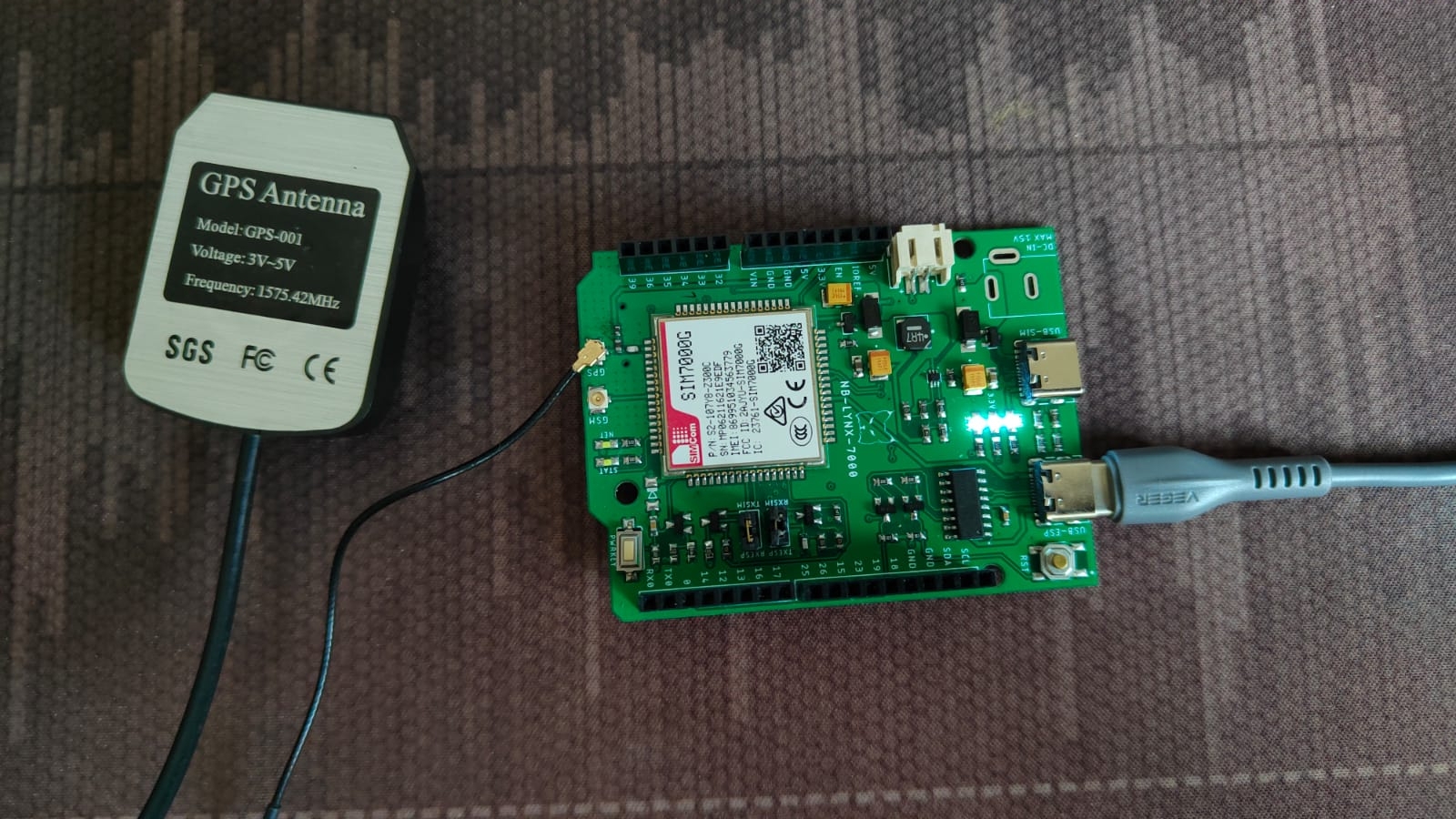
The first thing you need to do is to setup the equipment by connecting the NB-LYNX-7000 board with the GPS Antenna. The board can then be connected to your laptop/computer using a USB-C cable.
You need to connect the GPS Antenna to the GPS antenna port located on the NB-LYNX-7000 board.
Here are the equipment circuits that have been connected to a laptop/computer.

2. Launch Arduino IDE
3. Inputting programme code
To retrieve GNSS data, you need to input the programme code below in the Arduino IDE.
4. Programme Code Explanation
In order for the NB-LYNX-7000 board to communicate with the Antares platform, a SIM7000 module is used. SIM7000 is a cellular communication module developed by SIMCom Wireless Solutions. This module implements several protocols that allow the device to connect to the network using AT commands. The following describes some of the AT commands used in the programme code.
In the program code, the command "AT\r\n" is sent as the starting point or initialisation stage of the SIM7000 module. \r is a carriage return, while \n is a line feed. This command is sent to get an "OK" response.
In the programme code there is an "ATE0\r\n" command sent after getting an "OK" response. This command is used to disable echo mode indicating that initialisation has been successful.
In the programme code there is a command "AT+CGNSPWR=1\r\n" which is used to power control the GNSS module. Parameter "1" is used to switch on the GNSS power supply.
Here are other parameters that can be used.
0 = Switching off the GNSS power supply
1 = Switching on the GNSS power supply
In the programme code there is a command "AT+CGNSURC=1\r\n" which is used to display navigation data. Parameter "1" is used to display navigation data every time GNSS receives a signal from the satellite.
Here are some other parameters that can be used
0 = Turn off the displayed navigation data
1 = Displays navigational data every time the GNSS receives a signal
2 = Displays navigation data once every time the GNSS has received a signal for 2 times
…
256 = Displays navigation data once every time the GNSS has received a signal 256 times
5. Program Upload to NB-LYNX-7000 Board
Firstly, you must set up the board used by selecting ESP32 Dev Module under Tools > Board > esp32.
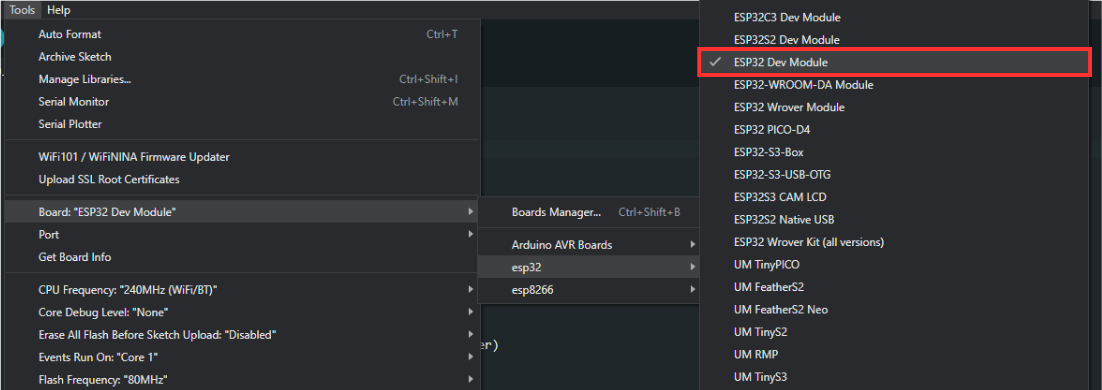
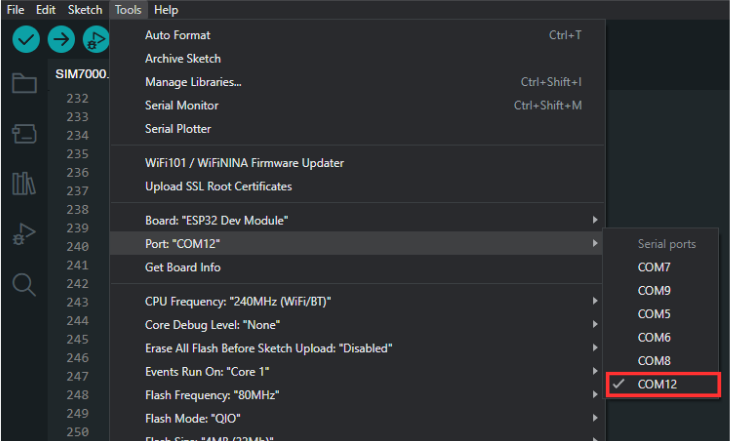
After that, you need to set the port used by going to Tools > Port > COM(X). The X value corresponds to the port number used by the NB-LYNX-7000 board.
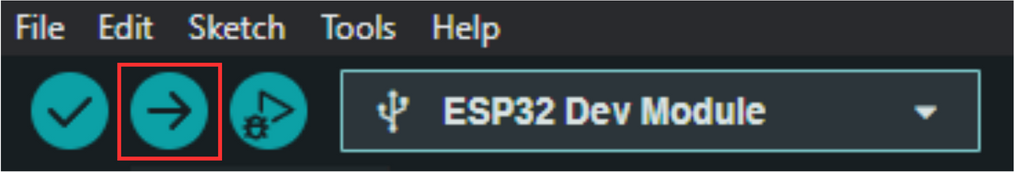
After you have prepared the programme code, you can then upload the programme code by pressing the upload button as shown in the image below.
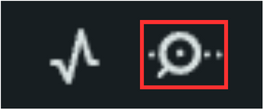
If the programme code has been uploaded successfully, you can open the Serial Monitor by pressing the icon as shown in the image below. You can find the icon on the top right-hand side.
You need to set the Serial Monitor's baud rate to 115200 so that its output can be read.
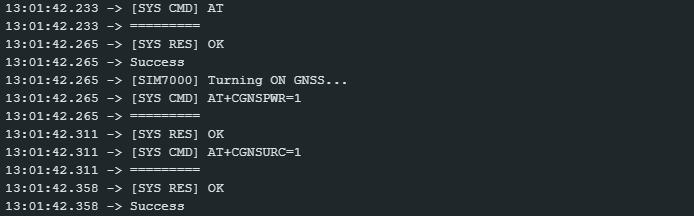
The Serial Monitor display will be as shown below which signifies the SIM7000 module initiation process and the process of turning on the GNSS to get navigation data.
Furthermore, the GPS Antenna will work to receive signals from satellites to obtain GNSS data in the form of navigation information consisting of latitude, longtitude, altitude, and date & time.
GPS Antenna sometimes takes a long time to receive signals from satellites until GNSS data is finally received. In this case, you can wait for a while.
If you have waited for a while but have not received GNSS data, it is likely that the GPS Antenna is not receiving enough signals from the satellites.
When the GPS Antenna is not receiving enough signals from the satellites, the display on the serial monitor will be as shown below.
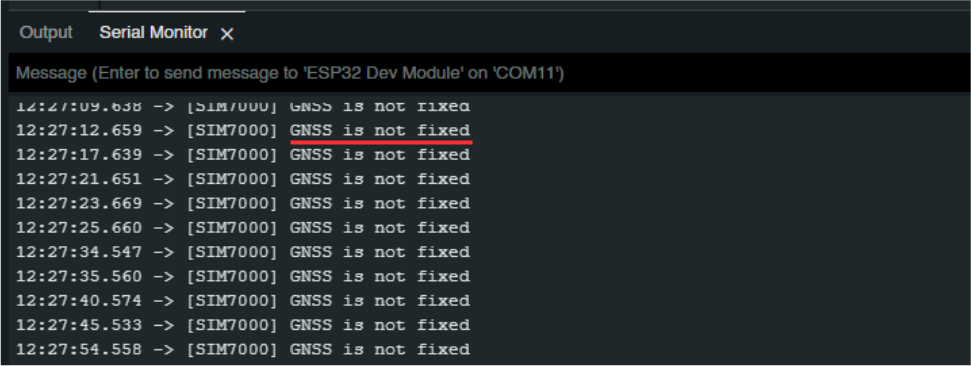
If the GPS Antenna is not receiving enough signal from the satellites, you can bring the GPS Antenna to an open room or by bringing it closer to a window.
When the antenna has received enough signal, the GNSS data will be displayed on the serial monitor as shown below.
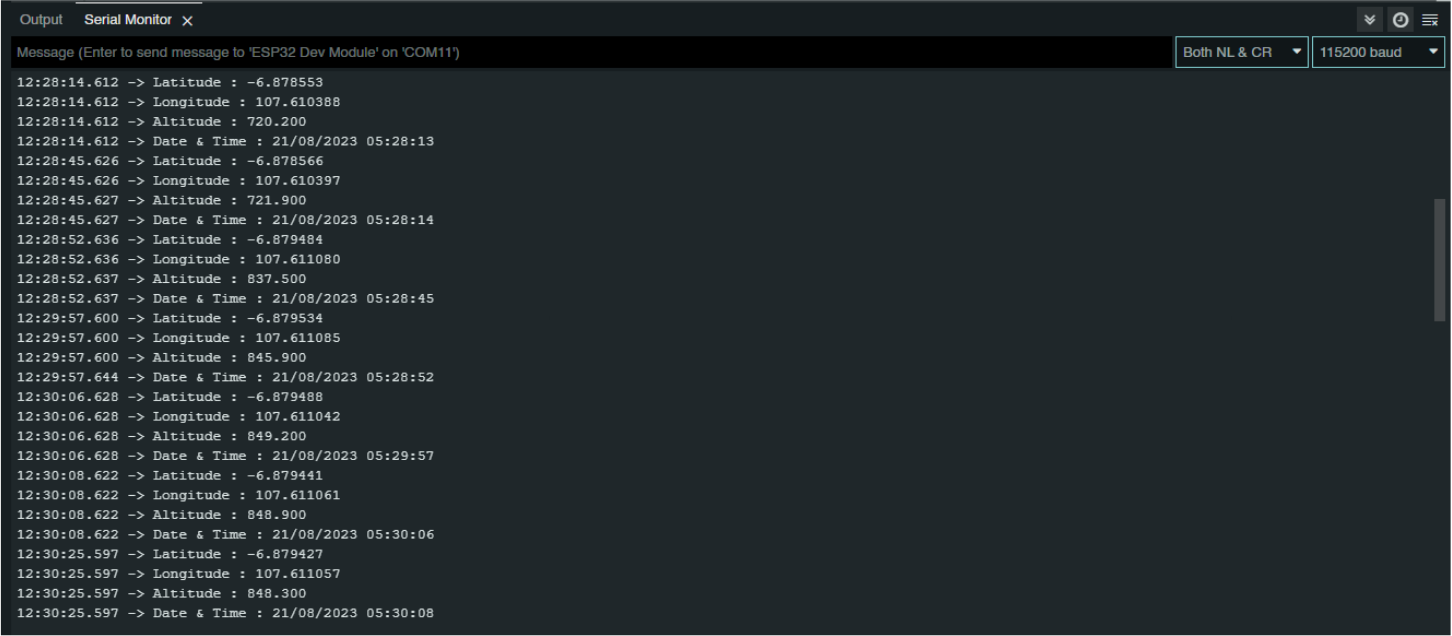
In this condition, the GPS Antenna will continuously receive signals from the satellite to display GNSS data on the serial monitor.
Last updated