Controlling Relays and LEDs Through Get Commands
In this project, you will use the Antares Shield Workshop on the ESP8266 module. In this Antares Shield Workshop, there are temperature, humidity (DHT11), relay, LED, and push button sensors. You will publish data using MQTTX which contains commands to control LEDs and relays. Then the ESP8266 Subscribes Data to the Antares IoT Platform which contains two command options, namely if the Relay input is 1 then the relay will turn on; Relay input is 0 then the relay will turn off; LED is 1 then the LED will turn on; LED input is 0 then the LED will turn off.

Prerequisites
The materials required follow the General Prerequisites on the previous page. If you have not prepared the requirements on that page, then you can visit the following page.
General Prerequisites ESP8266 Wi-FiThe additional materials specific to this project are as follows.
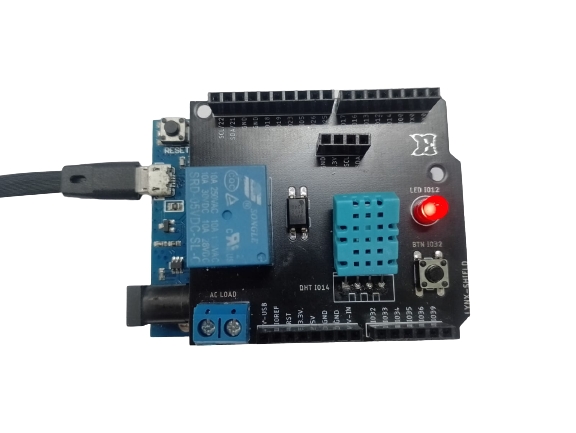
Shield Workshop Antares
Antares ESP MQTT Library. This documentation uses the Antares ESP MQTT library version 1.0.
MQTTX Software
Follow These Steps
1. Launch the Arduino IDE application
2. Opening Sample Programmem
Here is the programme code of the GET_DATA_RELAY_LED example.
3. Set WiFi Credential and Antares Credential in Program Code
Change the HTTP Protocol parameters in the following variables *ACCESSKEY, *WIFISSID, *PASSWORD, *projectName, and *deviceName. Adjust to the parameters in the Antares console.



4. Compile and Upload Program
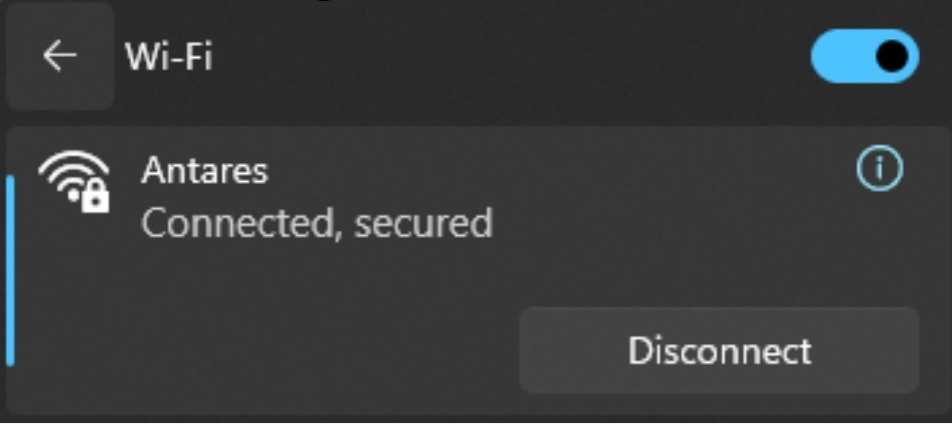
Connect the ESP8266 WEMOS D1R2 with your computer and make sure the Communication Port is read.
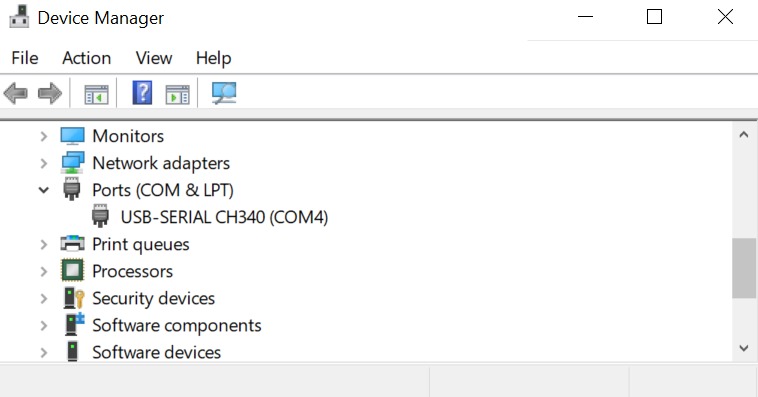
Set up the ESP8266 WEMOS D1R2 board by clicking Tools > Board > esp8266 in the Arduino IDE, then make sure the one used is LOLIN (WEMOS) D1 R2 & mini. Select the port according to the communication port that is read (in this case COM4). The result will look like the following picture.
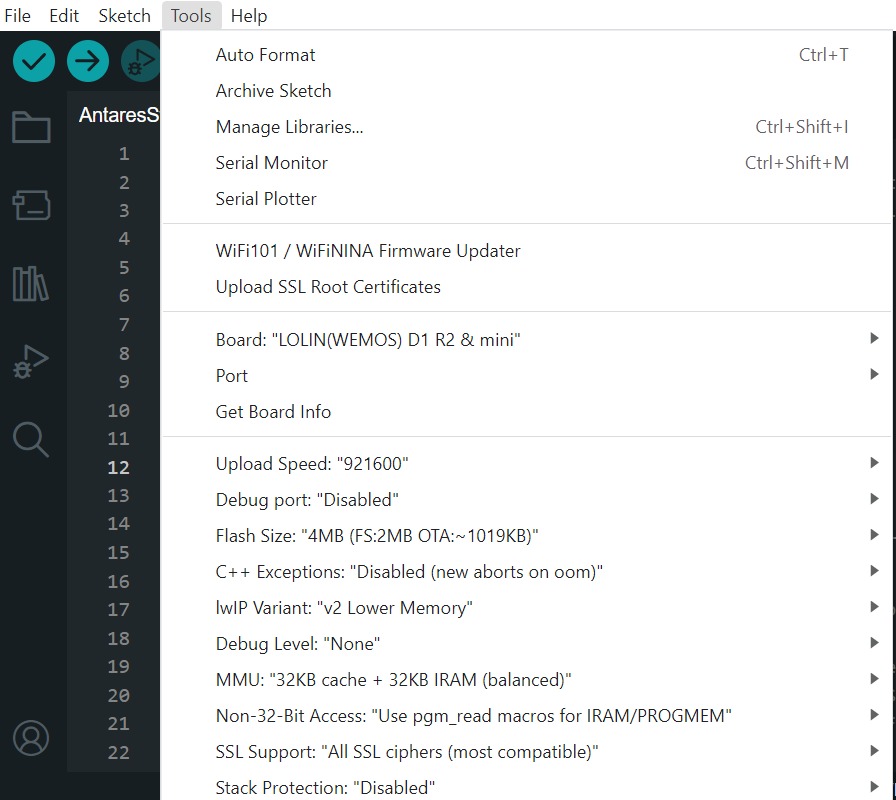
After all the setup is complete, upload the programme by pressing the arrow icon as shown below. Wait for the compile and upload process to finish.
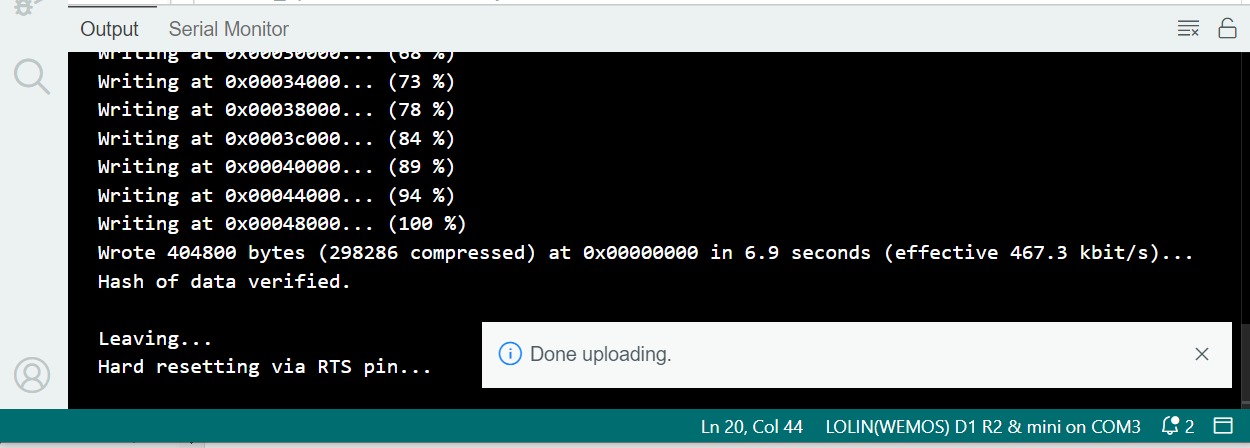
If the programme upload is successful, it will look like the following image..
After uploading the programme, you can view the serial monitor to debug the programme. The serial monitor icon is shown in the following image.

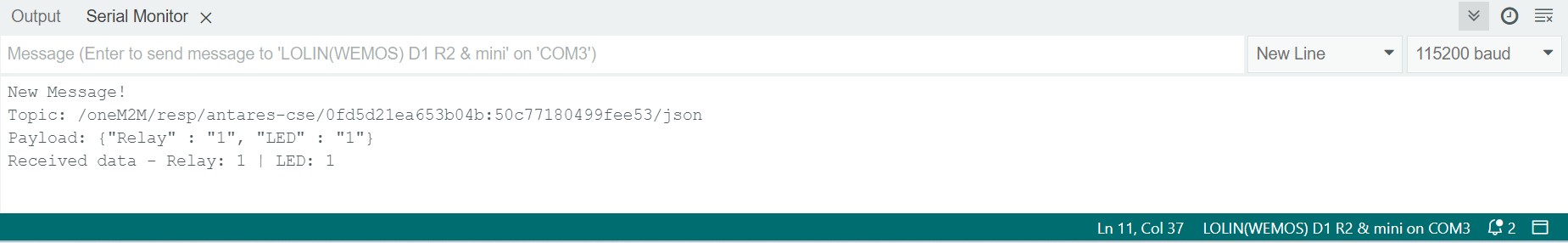
Set the serial baud rate to 115200 and select BothNL & CR. The result will look like the following image.
Make sure the serial baud rate matches the value defined in the programme code. If the serial baud rate is not the same between the programme code and the serial monitor, the ASCII characters will not be read properly.
5. Setup MQTTX Software
Open the MQTTX App, then select New Connection
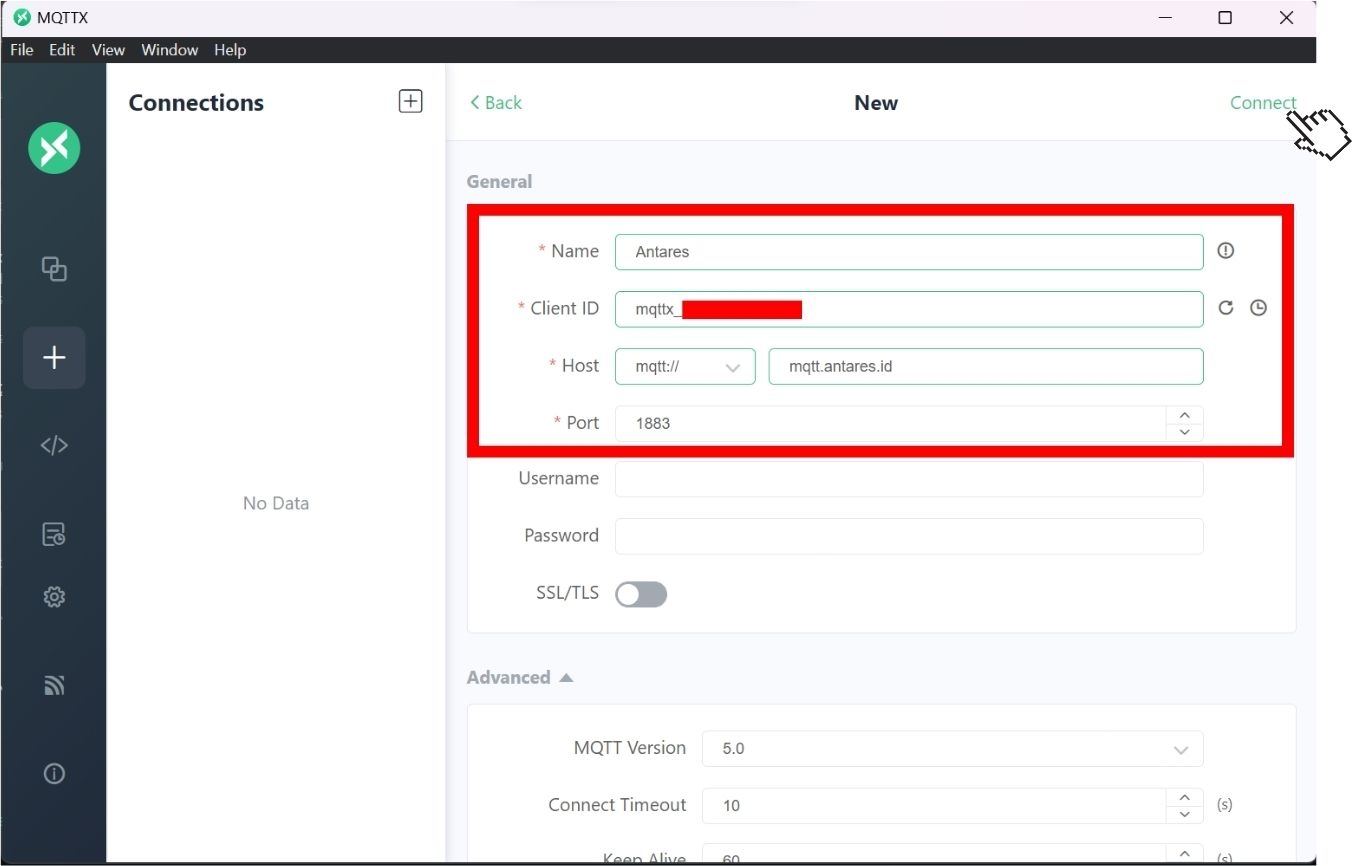
In order to configure MQTTX with Antares broker, adjust the Name, Host and Port as shown below, then click Connect.
If it is connected, there is a notification as shown below
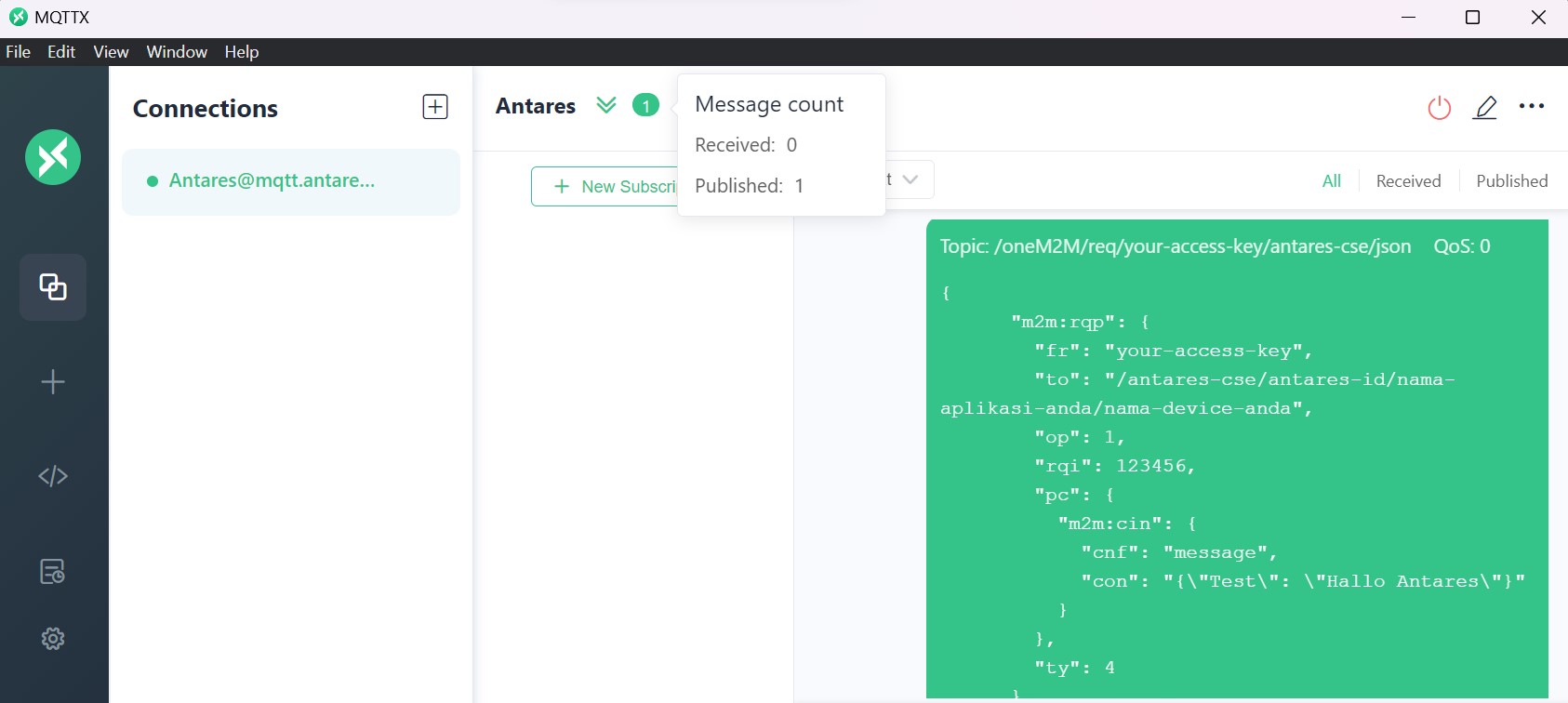
To publish to the Antares server, enter Topic and Payload in the fields in MQTTX.
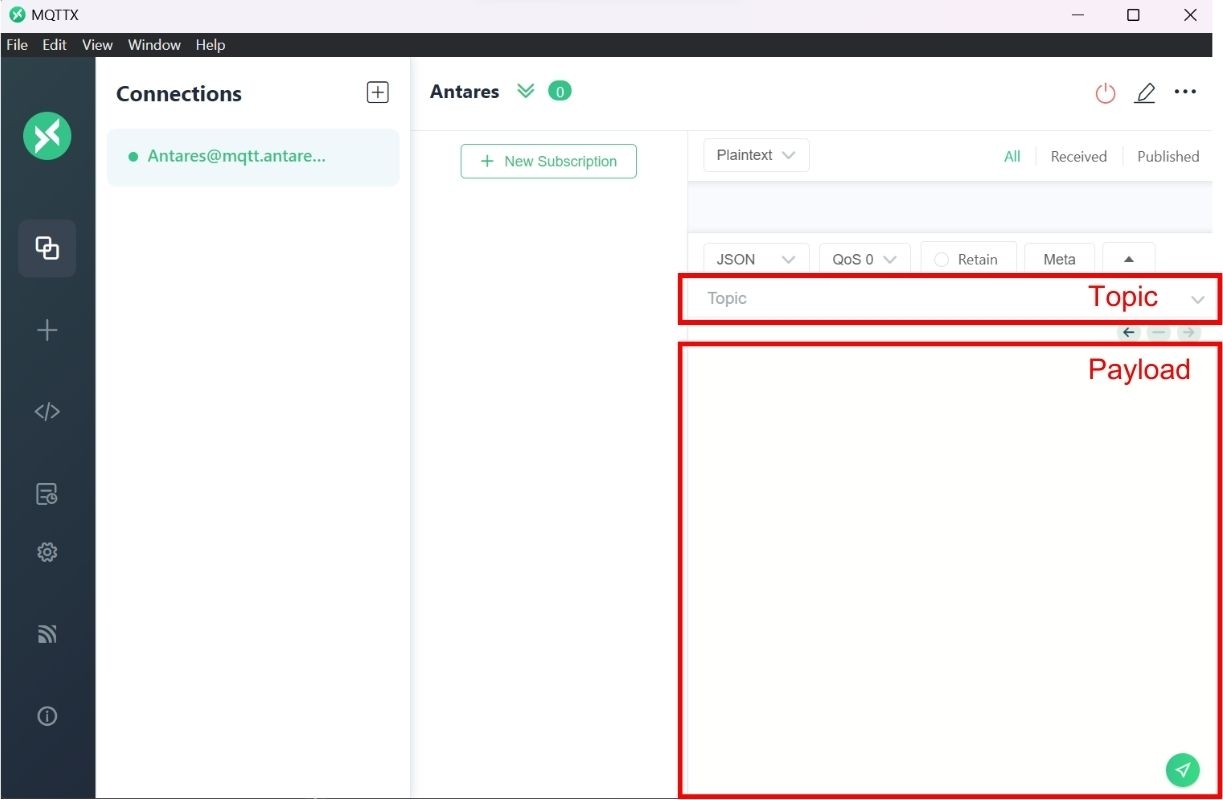
Topic
/oneM2M/req/your-access-key/antares-cse/json
Payload
In the MQTTX software, enter the Topic and Payload that you want to use. Then click Publish to send the message from MQTTX to the Antares server.
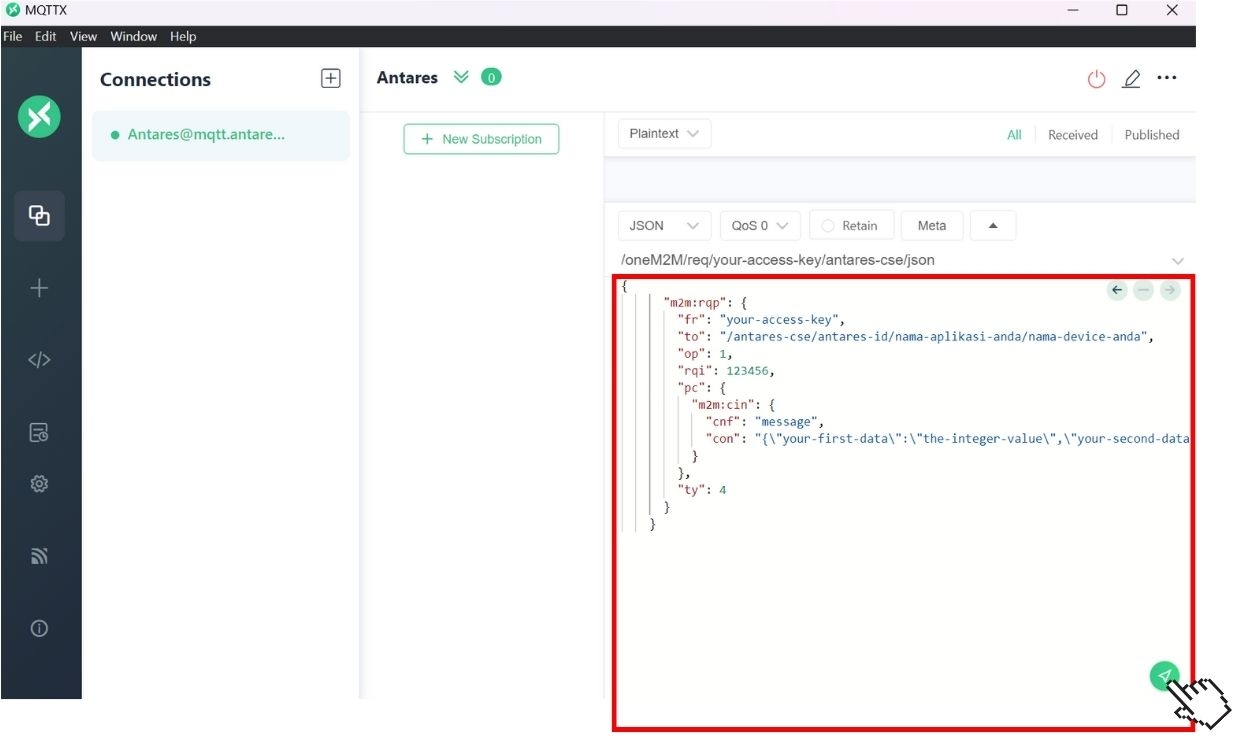
6. Sending MQTTX Messages to the Antares Server
After the MQTTX software setup is complete, it's time to send the PUBLISH command. The "Relay" field is filled with the string "1" for RELAY ON or "0" for RELAY OFF. The "LED" field is filled with the string "1" for LED ON or "0" for LED OFF. The "Relay" and "LED" fields are command messages to control the Relay and LED that will be sent via HTTP protocol to the Antares server.
If you have finished filling in the "Relay" and "LED" fields, then press the PUBLISH button on the MQTTX software located to the right of the Topic filling column, as shown below.
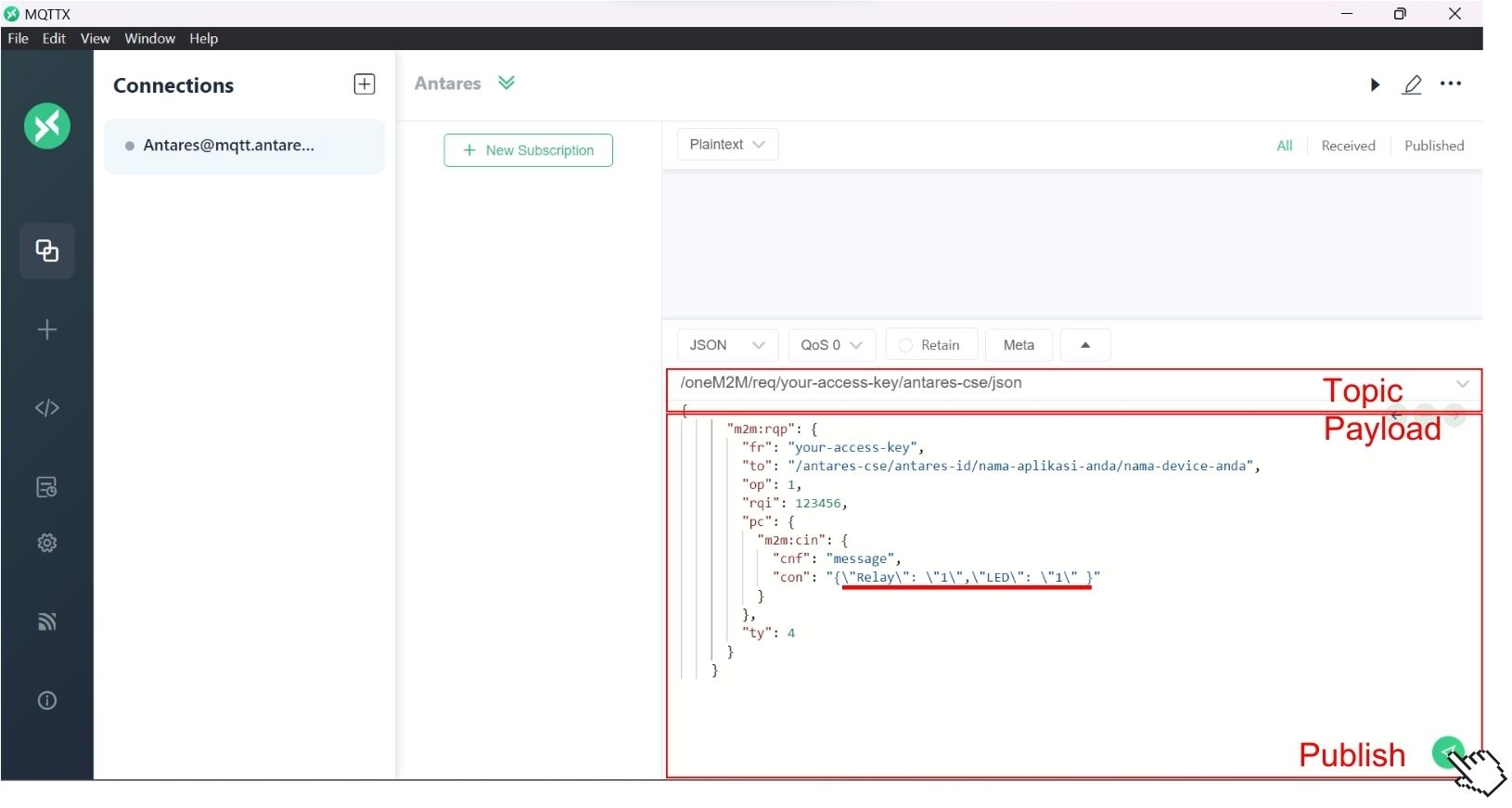
If it has been published, the MQTTX page will have a message like the following.
7.Check Data in Antares
After uploading the programme successfully, then open the device antares page and see if the data has been successfully sent.


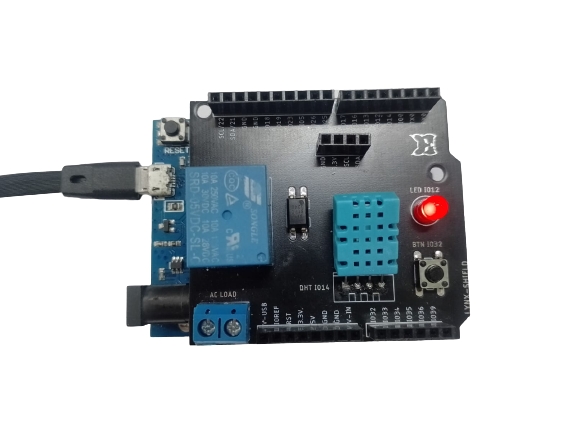
8. Output program
Get data from the Antares IoT Platform and display it on the OLED display after connecting to Wi-Fi is shown in the figure below:

Last updated