Sending Simple Data to Antares with HTTP Protocol
Prerequisites
General Prerequisites ESP32 Wi-FiFollow These Steps
1. Launch the Arduino IDE application
2. Opening Sample Programme
/*
This code will deploy data to your Antares project device with the following structure:
(Note that nesting the JSON object can only be done up to 2 levels using this library)
{
"temperature": random-int,
"humidity": random-int,
"wind_speed": random-float,
"rain_level": random-float,
"location" : {
"latitude": "static-string",
"longitude": "static-string"
}
}
For more information please visit https://antares.id/id/docs.html
*/
#include <AntaresESPHTTP.h>
#define ACCESSKEY "YOUR-ACCESS-KEY" // Replace with your Antares account access key
#define WIFISSID "YOUR-WIFI-SSID" // Replace with your Wi-Fi SSID
#define PASSWORD "YOUR-WIFI-PASSWORD" // Replace with your Wi-Fi password
#define projectName "YOUR-APPLICATION-NAME" // Replace with the Antares application name that was created
#define deviceName "YOUR-DEVICE-NAME" // Replace with the Antares device name that was created
AntaresESPHTTP antares(ACCESSKEY);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
antares.setDebug(true);
antares.wifiConnection(WIFISSID, PASSWORD);
}
void loop() {
// Variables
int temp = random(25,30) ;
int hum = random(75,90);
float windsp = float(random(20, 30))/3.33;
float rainlv = float(random(0, 20))/6.99;
String lat = "-6.8718189";
String lon = "107.5872477";
// Add variable data to storage buffer
antares.add("temperature", temp);
antares.add("humidity", hum);
antares.add("wind_speed", windsp);
antares.add("rain_level", rainlv);
antares.add("location", "latitude", lat);
antares.add("location", "longitude", lon);
// Send from buffer to Antares
antares.send(projectName, deviceName);
delay(10000);
}
3. Set HTTP Parameters in Programme Code




4. Compile and Upload Program
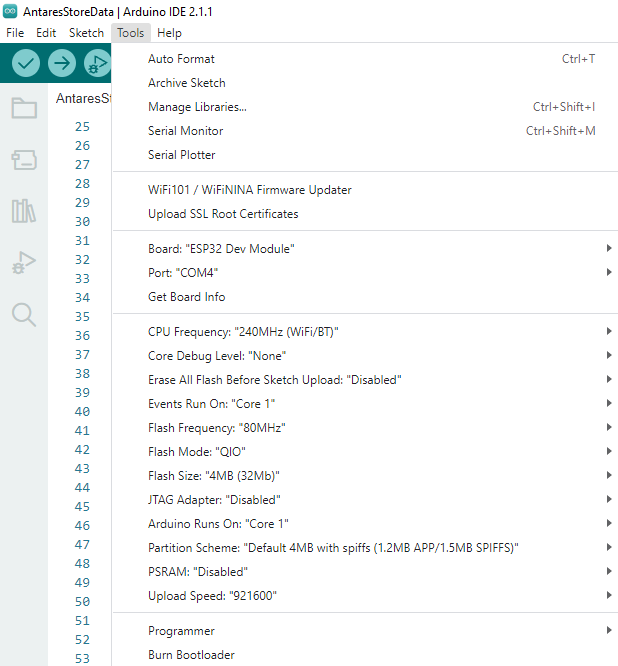
5. Check Data in Antares


PreviousESP32 (Wi-Fi) HTTP ProtocolNextRetrieve the Last Data from Antares Server with HTTP Protocol
Last updated